
Lowell (Wolf) Stadelman
Member since: 2020-02-02
90%
Overall KnocScore is higher than 90% of industry.
Users with equivalent metrics work at Apple Google and Facebook.
Supporting detailsEmployer: KNOC Inc.
Position: CEO and Founder
Education
University: University of Arizona
Major: Economics
Minor:
Various institutions including Stanford, Rice University, and UofI at Urbana Champaign
Major: Software Engineering
Military Service
Lowell (Wolf) Stadelman retired from the U.S. Army Special Forces as a Master Sergeant, E-8.
He served from 1986 to 2006.
.png)
Bio
Lowell (Wolf) Stadelman, began in the U.S. Army where he excelled and became a HALO qualified Special Forces Master Sergeant in just 16 years. Wolf's career included being a communications operator in the 1st Special Forces Operational Detachment-Delta, more commonly known as Delta Force. His work involved solving complex communication challenges in intense and extreme conditions and developing radio technologies under the leadership of one of the first unit members involved in Desert One. After 18 years of field and combat experience in multiple environments, Wolf was reassigned to a special office to develop new technology requirements.
Wolf's intense focus, and unique expertise were well suited for the field of research and development. His work led to the creation of new systems developed with gov't labs and entities such as Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, AeroVironment, and at universities such as MIT, Stanford, and UC Berkeley. Wolf's contributions provided the architecture and elements for products with a total estimated value of over a billion dollars.
After leaving Special Forces, Wolf became a Program Manager at Raytheon's Advanced Programs where he developed new technologies under one of the top physicists and thought leaders in the field. His inventions were adopted and carried out by DARPA, ARL, and other well recognized Gov't labs.
Wolf's philosophy always keeps him moving forward, and his curiosity continuously pushes for solutions that matter. He comes from a background firmly rooted in education. Growing up on a large engineering and science university, he developed a lifelong thirst for learning. While he was in the Army, Wolf attended college, and earned a 4.0 studying math and physics. Next, he studied economics at the University of Arizona. In his third round of higher education, in Southern California, Wolf studied software engineering. Since then, Wolf has applied for four patents and launched three technology companies.
Athletic Accomplishments
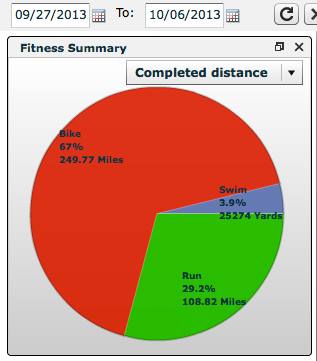
Lowell (Wolf) Stadelman is a competitive endurance athlete. He has completed 2 full distance Ironmans and finished in the top 7% of all competitors in 2013. His peak running events were two half-marathons that were completed in less than 90 minutes placing him in the top 2% of all half-marathon competitors. He claims to have completed a 160-mile bike event in 9 hours, and to have reached nearly 40 hours of training an 8-day training cycle while preparing for Ironman Arizona in 2013. It included over 108 miles of running, 249 miles of cycling, and 25 kilometers of swimming.
supporting details


Professional history and key individuals
-
The KnocScore
2024 - Present
detailsCEO Founder, Architect and Software Engineer. AI based
1. The only trusted source for Professional Knowledge and Skills validation.
2. A Credit Score for Knowledge
-
TopScholars - FlashMonkey Platform
2018 - Present
detailsTechnical Founder, Platform architect
Education Platform and knowledge credibility validation for higher-ed students
knocscore-container-service -
Contracts Angel
2013-2016
detailsFounder and Software Engineer
An AI Law-Tech startup that negotiated contracts for individuals and small companies.
-
-
Raytheon Missile Systems Advanced Programs
2006 to 2013
detailsProgram Manager developing new concepts in robotics and manned mobility.
AWARDED $4000 bonus for innovation in mil robotics
Authored the EM2 vehicle adopted by US Gov't for new development
-
US Army Special Operations
Prior to 2006
detailsServed as a 18E Communications and 18Z Operations Leader
KnocScore Metrics
ORIGIN SOURCE TRUST
Concrete
Guaranteed by others who have a meaningful stake or loss in their reputation
Some reputation gained and lost
Self reported and confirmed from existing data
Weak source of information
Software Engineering
Percentile:
Top 8%
at Apple Google and Facebook
Patents: |
4 |
Citations: |
7 |
What is a KnocScore™ :
KnoC™ is short for Knowledge Credibility.
Simple explanation
KnocScore is a credit Score for knowledge. Just as a credit score reflects an individual's financial reliability when applying for a loan, KnocScore reflects a professional's proven abilities within their field. When seeking employment, a higher KnocScore translates to superior performance capabilities, leading to better job prospects and terms. For instance, professionals with a higher KnocScore are more competitive and should have greater opportunities for career growth, increased responsibilities, and larger salary offers.
In order to achieve this, a KnoCSCore is defined by the following properties:
A KnocScore is a 'Gold Standard' for knowledge credibility that is provided by having qualities of 1) transparency, 2) derived in such a way that the evaluation cannot be manipulated to show false values, 3) void of irrelevant influence, 4) consistent, 5) show depth in specific domains of knowledge, 6) measure understanding using trusted methods of evaluation, 7) show that there is value through investment of a scarce resource, and 8) show value to the recipient firms and industries.
-
Categories of information is based on the method's of capture of the information. To provide the 'Gold Standard' from above, and guarantee that information cited, created, studied, or interacted with was by the individual in the report and contains no errors. Would be non-valuable if it was pure. Such information can be difficult to capture, but through some abstractions and judgment we can allow separate standards as long as it is understood appropriately. Thus, categories provides understanding and allows the use of concrete and non-concrete capture methods while providing understanding of its guarantee to prevent false values such as false claims. Categories are a vote of confidence as to the data's validity.
-
Category I is 'concrete' information that is directly captured by software that has met high standards to ensure that the data collected is free from errors and has not been manipulated to show false values. This includes third party software or software provided through our network. Category II and below are 'non-concrete' data.
-
Category II has the highest 'non-concrete' rating by being information guaranteed by others who have a meaningful stake or loss in their reputation if false values are given. This would be an organization such as IEEE that publishes documents and where credit is given to the data and author by citations and peer reviews. These acknowledgements provide a strong authority for knowledge credibility.
-
Category III is a non-concrete source of information, where a rating is related to a scarce resource such as a sales or captured business. Where the information reporting system has fewer means to ensure that the rated entity or individual is responsible for the sales or captured business, but there is reputation gained and lost if the information is inaccurate or the source is incorrect.
-
Category IV is non-concrete, self-reported information that has been confirmed by a data research firm. Where the information reporting system must rely on the research institutions guarantee and where the loss of the guarantee would be significant to the institution.
-
Category V is a weak source of information, where the rating comes from acknowledgement from others such as votes from a website or social media platform. There is little at risk for the rater when they give a false vote. There is no limit to a voter's domain expertise, e.g. anyone can vote, and frequently votes ar paid for by the thousands. This category remains important because it shows popularity. When tied to a value from a scarce resource, this can be strong although loose indicator. This category may be important to marketing.
-
-
Value denotes a concrete agreement that this knowledge is relevant and valuable for a specific knowledge domain. It is the amount others have paid for the knowledge that is created edited, studied, or interacted with practically. A lack of earnings does not denote a lack of value due to scarcity, timing, or demand. However, a positive number is a crowdsourced vote of confidence by peers and non-peers. Higher is generally better.
-
Hours represents time spent either creating, studying, in discussion such as video-lectures video-chat tutoring or in a study session, or in practice such as conducting activities related to a domain. E.g. writing software, managing a team, accounting, or painting a mural such as a muralist.
-
Points represents effort towards learning a knowledge domain in an academic setting. The KnocScore point system is non-standard. KnocScore incentives repetition and awards higher points for free-recall based questions. It also differs from a standard point system in that it deducts points when a question is answered incorrectly. Repeat questions when answered correctly will make up for the lost points. In some cases more points can be earned from repeat questions. Points should be considered as interaction with knowledge. In general a higher number indicates greater interaction and free-recall has been shown to be the strongest for memory retention.
-
Publications, Patents, and Citations represent acknowledged documents that have been authored or co-authored by the individual. These are documents that show expertise and agreement. This is Category II information since historically, plagiarism has plagued organizations that reward publishing such documents. Citations are acknowledgement from peers and provide credibility to the information's validness. This is recognized as showing the individuals competence within a domain.
-
Domain percentile by organization is a selectable field that provides an apples-to-apples comparison of individuals regardless of the organization they are associated with. This field allows two individuals from different universities to be compared and provides an analysis of all captured data for the individuals in that organization.
-
Skills requested by Industry provides an indicator as to the individuals readiness as provided by industry's requests for the skills they look for. This helps firms understand where an individual stands in regards with their industry.
-
Works at and Hired By provides hiring managers an understanding of the competence of individuals when peers with similar metrics are hired by large organizations.